Windows 11 is designed to be a more modern, secure, and user-friendly operating system than Windows 10. Here are some of the values of Windows 11:
- A new Start menu: The Start menu in Windows 11 is more centered and simplified, with pinned apps and recent files at the top. You can also search for apps and files directly from the Start menu.
- Widgets: Widgets are back in Windows 11! They're small, interactive windows that you can pin to the side of your screen. Widgets can show you news, weather, sports scores, and more.
- Snap Layouts: Snap Layouts make it easy to multitask on Windows 11. You can snap windows into different layouts, such as 2x2, 3x1, or 4x1. This helps you to keep your work organized and efficient.
- Teams Chat: Teams Chat is integrated into the Windows 11 taskbar, so you can easily chat with your friends and colleagues. You can also use Teams to make video calls and voice calls.
- Multitasking improvements: Windows 11 has a number of multitasking improvements, such as the ability to create multiple desktops and the ability to snap windows more easily. These improvements make it easier to stay organized and productive on Windows 11.
- Gaming enhancements: Windows 11 has a number of gaming enhancements, such as support for Auto HDR and DirectStorage. Auto HDR enhances the visual quality of games on HDR-compatible displays, while DirectStorage speeds up loading times for games.
These are just a few of the best features of Windows 11. If you're looking for
Windows 11 is designed to be a more modern, secure, and user-friendly operating system than Windows 10. Here are some of the values of Windows 11:
- Simplicity: Windows 11 is designed to be easy to use, with a simplified Start menu, taskbar, and settings app.
- Security: Windows 11 includes a number of security features, such as hardware-based security, Secure Boot, and Windows Hello.
- Modernity: Windows 11 has a modern design that is more in line with other modern operating systems, such as macOS and Chrome OS.
- Performance: Windows 11 is designed to be more efficient than Windows 10, with better battery life and faster boot times.
- Gaming: Windows 11 is optimized for gaming, with features such as Auto HDR and DirectStorage.
Here are some of the things that could be improved in Windows 11:
- Compatibility: Some older apps and devices may not be compatible with Windows 11.
- Customization: Windows 11 is not as customizable as Windows 10, with fewer options for changing the look and feel of the operating system.
- Privacy: Some users have raised concerns about the privacy implications of some of the features in Windows 11, such as the use of telemetry data.
Overall, Windows 11 is a solid operating system that offers a number of improvements over Windows 10. However, there are still some areas where it could be improved.
- ipconfig: This command displays your network configuration.
The ipconfig command is a command-line utility that displays your network configuration. It can be used to view your IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and other network settings.
To use the ipconfig command, open a command prompt window and type the following command:
ipconfig
This will display your basic network configuration, including your IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
You can also use the ipconfig command to view more detailed network information. For example, you can use the following command to view your DNS server settings:
ipconfig /all
This will display all of your network settings, including your IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server addresses, and other information.
The ipconfig command is a powerful tool that can be used to troubleshoot network problems. If you are having trouble connecting to the internet or other network resources, you can use the ipconfig command to view your network configuration and identify the source of the problem.
Here are some of the most common options for the ipconfig command:
- /all: This option displays all of your network settings, including your IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server addresses, and other information.
- /release: This option releases your current IP address and DHCP lease.
- /renew: This option renews your current IP address and DHCP lease.
- /flushdns: This option flushes the DNS resolver cache.
- /registerdns: This option registers your computer's DNS names with the DHCP server.
- ping: This command tests the connectivity to a remote host.
The ping command is a command-line utility that tests the connectivity to a remote host. It sends a series of packets to the remote host and waits for a response. If the remote host responds, the ping command will display the round-trip time (RTT) for each packet. The RTT is the time it takes for a packet to travel from your computer to the remote host and back.
To use the ping command, open a command prompt window and type the following command:
ping google.com
This will send 4 packets to the Google website and display the RTT for each packet. If the Google website is reachable, you will see output similar to the following:
C:\Users\bard>ping google.com
Pinging google.com [142.250.190.100] with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 142.250.190.100: bytes=32 time=12ms TTL=112
Reply from 142.250.190.100: bytes=32 time=11ms TTL=112
Reply from 142.250.190.100: bytes=32 time=11ms TTL=112
Reply from 142.250.190.100: bytes=32 time=11ms TTL=112
Ping statistics for 142.250.190.100:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:Minimum = 11ms, Maximum = 12ms, Average = 11msIf the remote host is not reachable, you will see output similar to the following:
C:\Users\bard>ping google.com
Pinging google.com [142.250.190.100] with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Ping statistics for 142.250.190.100:Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0msThe ping command can be used to troubleshoot network problems. If you are having trouble connecting to a website or other network resource, you can use the ping command to see if the remote host is reachable. You can also use the ping command to test the speed of your internet connection.
Here are some of the most common options for the ping command:
- /t: This option tells the ping command to send packets continuously until you press Ctrl+C.
- /n: This option tells the ping command to send a specified number of packets.
- /l: This option tells the ping command to use a specified size for the packets.
- /v: This option tells the ping command to display verbose output.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any other questions.
- tracert: This command traces the path to a remote host.
- netstat: This command displays network connections.
- tasklist: This command displays a list of running processes.
These commands can be used to troubleshoot network problems, diagnose performance issues, and manage your computer's resources.
After moving away from the corporate work-style, Alex has found rewards in a lifestyle of constant analysis, team coordination and pestering his colleagues. Holding an MCSA Windows Server... read more
- The Registry Editor is a powerful tool in Windows OS that allows users to view and modify a database that stores configuration settings.
- Modifying the registry should be done with caution, as incorrect changes can cause serious OS problems and even prevent it from booting.
XINSTALL BY CLICKING THE DOWNLOAD FILE
- Download and Install Fortect on your PC
- Launch the tool and Start scanning to find broken files that are causing the problems
- Right-click on Start Repair to fix issues affecting your computer’s security and performance
- Fortect has been downloaded by 0 readers this month.
The Windows Registry is a database of configuration settings for the Windows operating system and the software that runs on it. It’s an essential part of the system, as it stores information about hardware, software, and user settings.
If you want to customize your Windows 11 computer or troubleshoot problems, you’ll need to know how to use the Registry Editor, which allows you to view and edit the Registry.
In this article, we’ll show you how to access Registry Editor in Windows 11 and provide tips for using it safely and effectively.
How do I get into Registry Editor?
Now you have gotten into the tool, let us explore some tips for using Registry Editor as well as a few common tasks.
How can I use Registry Editor safely and effectively?
1. Make a backup
It’s crucial to make a backup of the registry before making any modifications. In the event that any issues arise as a consequence of your modifications, this will enable you to restore the register to an earlier state.
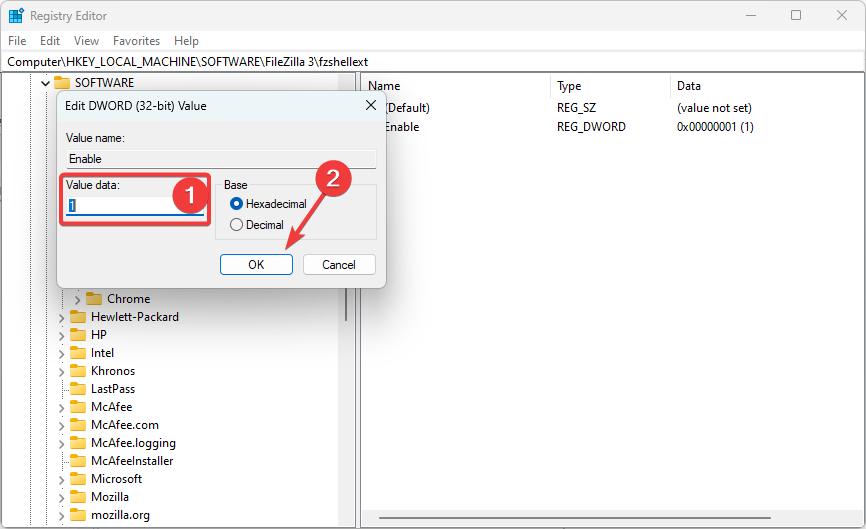
2. Modify values
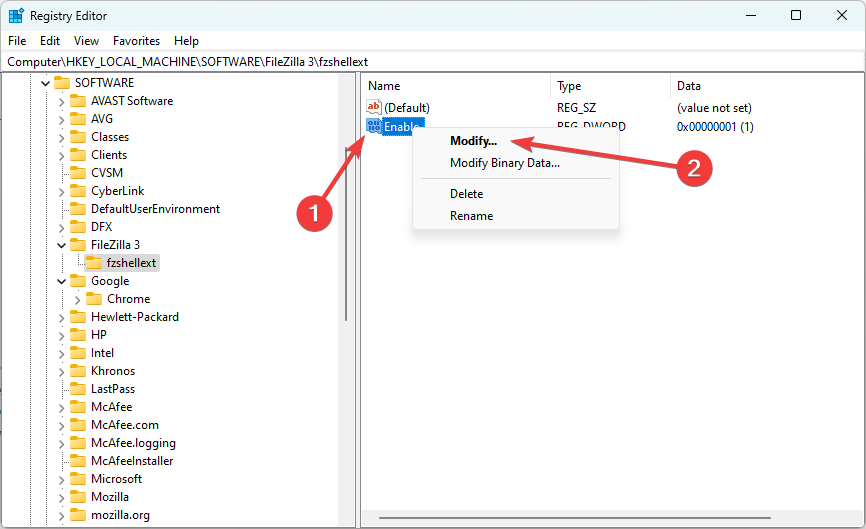
- Open up the Registry Editor, and navigate to the value you want to modify (The modifiable elements will be displayed on the right pane after you have selected a key).
- Right-click on any of these elements and select Modify (you may also choose Modify Binary Data).
- Now enter the new values needed in the Value Data text fields and click OK.
Be careful when modifying values; be sure to enter the correct data type and value. Incorrect data types or values can cause problems with the operating system or applications.
Remember to only make changes to the registry if you are sure they are necessary, since unnecessary changes can increase the risk of encountering problems.
3. Add values
- Open up the Registry Editor, and navigate to any key where you want to add a new value.
- Click on any empty space on the right pane, hover over New, then select any of the value types you wish to add.
- Name the newly created value. Then modify it accordingly using the steps shown in the Modifying values section.
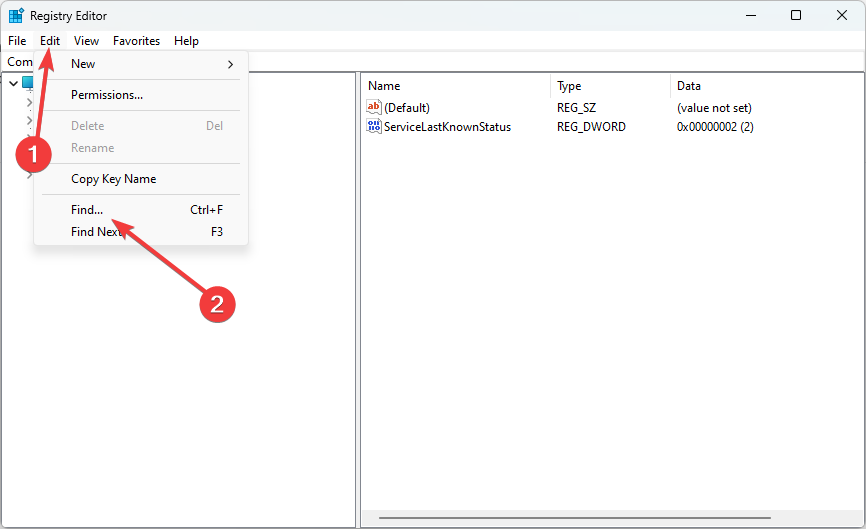
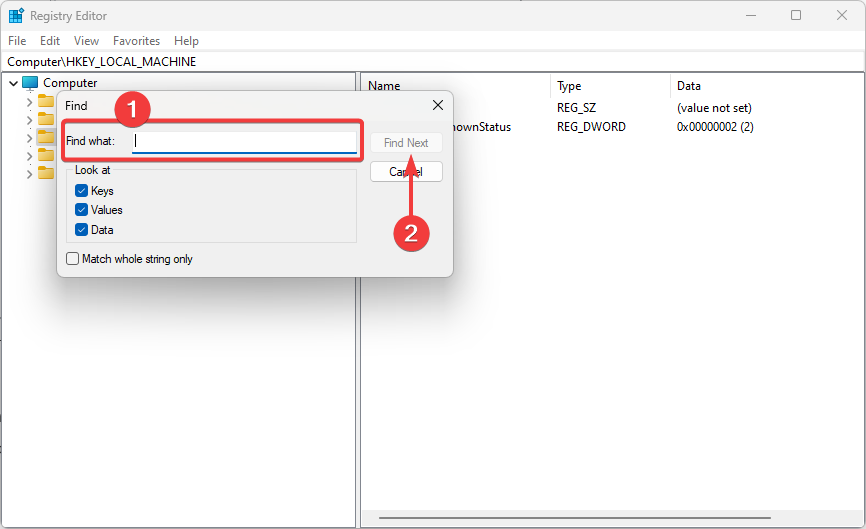
4. Use the Registry Editor search function
The Registry Editor includes a search function that allows you to find specific keys or values within the registry. This can be helpful if you are looking for a specific setting or if you are trying to troubleshoot a problem.
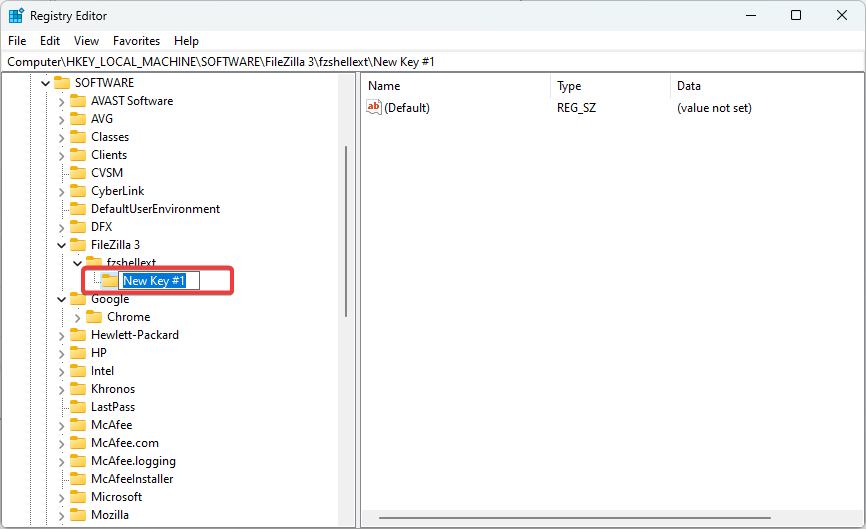
5. Add Registry keys
- Launch the Registry Editor.
- Navigate to the path where you wish to add the new key. In our case we have navigated to the path below:Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\FileZilla 3\fzshellext
- Right-click on the element, hover on New, and select Key.
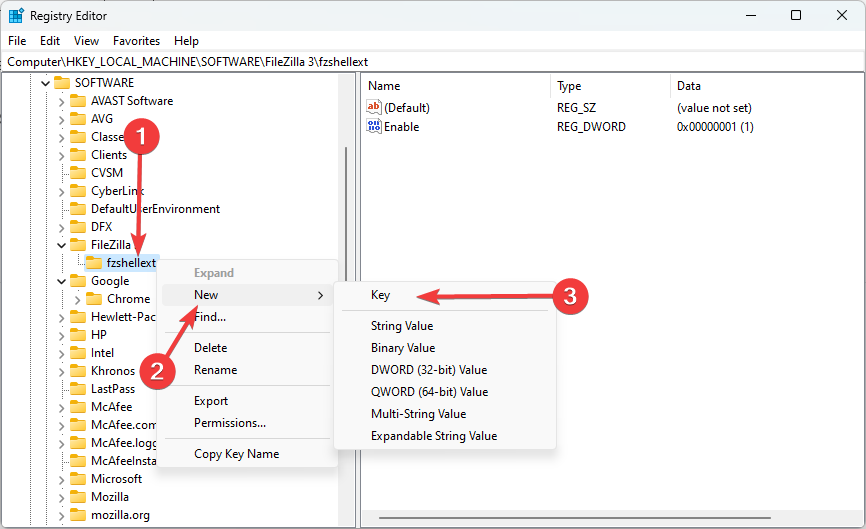
- Name the key. In our case, we call it New Key #1.
- Now you can edit values for this key using the same process explained in the Modifying values section.
6. Deleting values
- Launch the Registry Editor.
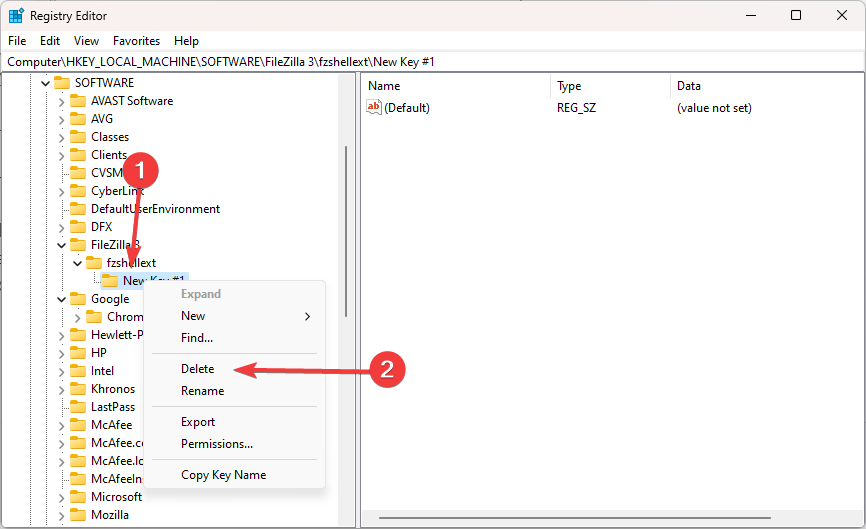
- Navigate to the key you wish to delete. In our case we have navigated to the path below (the new key we created in the section above):Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\FileZilla 3\fzshellext\New Key #1
- Right click on the key and select Delete.





No comments:
Post a Comment