Make a big analysis with examples of the ways in which computers can be used to make their daily work easier in the present and in the future.
Data Processing and Analysis:
1.Computers can handle vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, enabling efficient data processing, analysis, and reporting. For instance, financial institutions use computers to process and analyze large volumes of transactional data for fraud detection and risk assessment.
2.In the future, with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, computers will be able to automate complex data analysis tasks. For example, healthcare professionals can use AI-powered systems to analyze medical records and diagnostics to provide accurate treatment recommendations.
Communication and Collaboration:
1.Computers enable seamless communication and collaboration among individuals and teams. Email, instant messaging, and video conferencing platforms facilitate real-time communication, irrespective of geographical locations.
2.Future developments in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) could enhance collaboration further. For instance, architects and engineers can use AR to visualize and modify designs collaboratively in a virtual workspace.
Automation and Efficiency:
3.Computers automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, freeing up human resources for more complex and creative work. Manufacturing industries use computers to control assembly lines, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
4.In the future, automation will expand to various sectors, such as transportation and logistics. Self-driving vehicles and smart traffic management systems will optimize routes, minimize congestion, and enhance overall transport efficiency.
Information Storage and Retrieval:
1.Computers provide convenient and reliable storage for vast amounts of information. Document management systems and cloud storage services allow easy access to files from anywhere, promoting flexibility and remote work.
2.As data storage capacities increase, future computers will enable more extensive knowledge repositories. For example, researchers can access comprehensive databases to aid scientific discoveries and innovation.
Personal Assistance and Productivity Tools:
1.Computers serve as personal assistants, organizing schedules, setting reminders, and providing access to various productivity tools. Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant can perform tasks based on voice commands.
2.In the future, personal assistants will become more intelligent and context-aware, offering proactive suggestions and automating routine tasks. They may even have the ability to anticipate users' needs and preferences.
Simulation and Modeling:
1.Computers allow simulation and modeling of complex systems, enabling experimentation and analysis without real-world repercussions. For example, engineers can simulate the behavior of structures under different conditions to optimize designs.
2.Future advancements may lead to more accurate and sophisticated simulations. For instance, climate scientists can use advanced computational models to predict weather patterns with higher precision, aiding disaster management and agriculture.
Creative Work and Innovation:
1.Computers provide tools and software for creative work, such as graphic design, video editing, and music production. Creatives can leverage powerful software like Adobe Creative Suite to bring their ideas to life.
2.In the future, computers may possess enhanced creativity capabilities. AI-powered systems can generate art, music, and literature, collaborating with human creators to produce unique and innovative works.
Make a big analysis with examples of the ways in which computers can be used to make their daily work easier in the present and the future.
1.Data Processing and Analysis:\
Computers excel at processing and analyzing vast amounts of data swiftly and accurately. In the present, financial institutions rely on computer systems to detect fraud and assess risks by analyzing extensive transactional data. Looking ahead, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will empower computers to automate complex data analysis tasks. For instance, AI-powered systems can analyze medical records and diagnostics to provide precise treatment recommendations, revolutionizing healthcare
- 2.Communication and Collaboration:Computers have significantly enhanced communication and collaboration, breaking down geographical barriers. Email, instant messaging, and video conferencing platforms enable real-time interactions, fostering seamless collaboration. The future holds even more exciting prospects, as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies evolve. Architects and engineers, for instance, can utilize AR to collaboratively visualize and modify designs in a virtual workspace, boosting efficiency and creativity.
- 3.Automation and Efficiency:Automation is a key strength of computers, enabling the delegation of repetitive and time-consuming tasks to machines. This frees up human resources for more complex and creative work. Manufacturing industries have long relied on computer-controlled assembly lines to minimize errors and enhance efficiency. Looking forward, automation will extend to various sectors, including transportation and logistics. Self-driving vehicles and smart traffic management systems will optimize routes, reduce congestion, and revolutionize transport efficiency.
- Information Storage and Retrieval:Computers have revolutionized information storage, offering secure and accessible solutions. Document management systems and cloud storage services allow easy access to files from anywhere, facilitating flexible and remote work arrangements. As data storage capacities continue to expand, future computers will enable vast knowledge repositories. Researchers will have access to comprehensive databases, propelling scientific discoveries and innovation to unprecedented heights.
- 4.Personal Assistance and Productivity Tools:Computers serve as personal assistants, organizing schedules, setting reminders, and providing access to a wide array of productivity tools. Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant have become ubiquitous, performing tasks based on voice commands. Looking ahead, personal assistants will become more intelligent and context-aware. They will offer proactive suggestions, automate routine tasks, and even anticipate users' needs and preferences, supporting individuals in their daily work.
- 5.Simulation and Modeling:Computers empower professionals to simulate and model complex systems, enabling experimentation and analysis without real-world repercussions. Engineers, for example, can simulate the behavior of structures under various conditions to optimize designs. In the future, advancements in computational power will enable more accurate and sophisticated simulations. Climate scientists will leverage advanced computational models to predict weather patterns with higher precision, aiding disaster management and agricultural planning.
- 6.Creative Work and Innovation:Computers provide powerful tools and software for creative work, such as graphic design, video editing, and music production. Creatives leverage software like Adobe Creative Suite to bring their ideas to life. Looking to the future, computers may possess enhanced creativity capabilities. AI-powered systems can generate art, music, and literature, collaborating with human creators to produce unique and innovative works that push the boundaries of creativity.
What are the merits and demerits of using computers to make our work easier?
Using computers to make our work easier offers numerous merits, but it also comes with certain demerits. Let's explore both sides:
Merits:
Increased Efficiency: Computers can automate repetitive tasks, perform complex calculations, and process large volumes of data at high speeds. This enhances efficiency and allows for faster completion of work, leading to increased productivity.
Accuracy and Precision: Computers excel at performing tasks with a high level of accuracy and precision. They minimize human errors and ensure consistent and reliable results, particularly in data analysis, simulations, and complex calculations.
Time Savings: Computers can significantly reduce the time required to complete tasks. Automation, streamlined processes, and quick access to information save valuable time, allowing individuals to focus on more critical and creative aspects of their work.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: Computers facilitate seamless communication and collaboration. Instant messaging, video conferencing, and collaborative platforms enable real-time interactions, irrespective of geographical distances. This promotes efficient teamwork and knowledge sharing.
Access to Information: Computers provide easy access to vast amounts of information. Online databases, search engines, and cloud storage services allow quick retrieval of relevant data, fostering informed decision-making and promoting knowledge sharing.
Demerits:
Dependency and Reliability: Overreliance on computers can become a drawback when technical issues arise. System failures, software glitches, or cybersecurity breaches can disrupt workflow, leading to downtime and potential loss of productivity.
Learning Curve and Training: Introducing new computer systems or software may require employees to undergo training and overcome a learning curve. This initial investment in time and resources can be a challenge, particularly for individuals who are less familiar with technology.
Job Displacement and Skills Gap: Automation and computerization can lead to job displacement as certain tasks are taken over by machines. This can result in unemployment or the need for workers to acquire new skills to remain relevant in the evolving job market.
Security and Privacy Risks: Storing sensitive data on computers increases the risk of security breaches and privacy violations. Cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access can have severe consequences, including financial losses and damage to reputation.
Physical and Mental Health Issues: Prolonged computer use can lead to physical health issues such as eye strain, repetitive strain injuries, and sedentary lifestyle-related problems. Additionally, excessive screen time and constant connectivity can contribute to mental health issues like stress, anxiety, and social isolation.
Technological Obsolescence: Computers and software quickly become outdated as technology advances. This necessitates continuous investments in upgrading hardware and software to stay current, which can be costly and time-consuming.
What methods can be used to facilitate work through the computer?.
Several methods can be used to facilitate work through computers. Here are some common methods:
Automation:
Automation involves using computer programs or scripts to perform repetitive or routine tasks automatically. This can include tasks such as data entry, report generation, file organization, and email management. Automation tools and scripting languages, such as Python or PowerShell, can be utilized to streamline workflows, save time, and reduce human error.
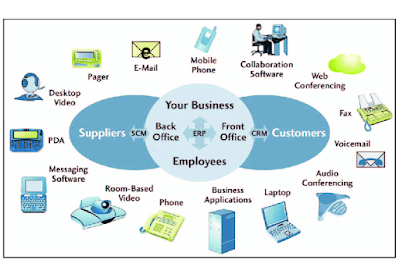
Collaboration and Communication Tools:
Computers offer a wide range of collaboration and communication tools that facilitate effective teamwork and information sharing. These tools include email clients, instant messaging platforms, video conferencing software, project management systems, and shared document repositories. By utilizing these tools, individuals and teams can communicate, collaborate, and share information seamlessly, regardless of geographical locations.
Project Management Software:
Project management software helps plan, organize, and track project tasks, resources, and timelines. These tools provide features like task assignment, progress tracking, milestone management, and document sharing. Project management software enables efficient coordination, enhances productivity, and ensures effective project execution.
 Cloud Computing:
Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing enables remote storage and access to data and applications over the internet. With cloud-based services, individuals and organizations can store, share, and collaborate on files and documents from anywhere, using any device. Cloud computing also offers scalability, cost-efficiency, and data backup, reducing the need for local infrastructure and enhancing flexibility.
Task and Time Management Tools:
Task and time management tools help individuals organize their work, set priorities, and manage deadlines. These tools often include features like to-do lists, reminders, calendars, and time tracking. Task and time management tools assist in optimizing productivity, managing workloads, and ensuring efficient utilization of time and resources.
Data Analysis and Visualization Software:
Computers provide powerful data analysis and visualization tools that enable users to extract insights from complex datasets. Software like Microsoft Excel, Tableau, or Python libraries like Pandas and Matplotlib allow for data manipulation, analysis, and visualization. These tools assist in making data-driven decisions, identifying trends, and communicating findings effectively.Virtualization and Remote Desktop:
Virtualization technology allows running multiple operating systems or applications on a single physical computer. It enables users to create virtual machines or desktops, providing flexibility and resource optimization. Remote desktop solutions enable accessing a computer or virtual desktop remotely, facilitating remote work and collaboration.Personal Productivity Tools:
Computers offer a wide array of personal productivity tools, including word processors, spreadsheets, presentation software, note-taking applications, and personal information managers. These tools help individuals create, organize, and manage their work-related documents and information efficiently.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) enable computers to automate tasks, make predictions, and derive insights from data. AI-powered tools and algorithms can assist in various domains, such as natural language processing, image recognition, data analysis, and customer support, augmenting human capabilities and enhancing productivity.
Custom Software Development:
In some cases, organizations develop custom software applications tailored to their specific workflows and requirements. Custom software development allows for the creation of specialized tools and systems that align with unique business processes, increasing efficiency and effectiveness.




.jpeg)

.jpeg)
.jpeg)




No comments:
Post a Comment